Overcoming 5G Data Challenges to Realize Its Potential
Recently, Hale Donertasli, Cloud Architect at Rakuten Mobile, presented the talk “5G and Data Challenges”. In the talk, Hale describes the new innovations that will become possible because of 5G and its impressive data rate that will eventually achieve 20Gbps. Underpinning this achievement in speed is a cloud native, service-based architecture. But enhancing data and network speed and reliability while adopting microservices in the cloud doesn’t come without some challenges to address and overcome. Hale describes the 5G data challenges in the current landscape, and then proposes solutions to those challenges to be able to fully realize the potential of what 5G can unlock for people everywhere.
What Is 5G?
5G is the 5th generation mobile network. 5G wireless technology delivers higher multi-Gbps peak data speeds, ultra low latency, more reliability, and massive network capacity. The higher performance and improved efficiency of 5G will make it possible to more seamlessly connect not only users, but machines, objects, and devices.
5G Enables Innovation
Hale opens with setting the stage of what will become possible because of 5G technology, noting that 5G will expand the mobile ecosystem.

“All these things, and many more could become our day to day reality with the power of 5G. It is predicted that the connectivity of 5G technology changes everything from our health and wellbeing to transport and manufacturing processes. All this revelation happens due to 5G service-based architecture,” explained Hale.
A Look into the 5G Service Based Architecture
An industry consortium called 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) is responsible for setting standards for mobile telecommunications, including 5G. 3GPP defines a 5G service based architecture made up of interconnected Network Functions (NFs), with each having access to the others’ services. The storage layer that is inclusive of subscriber-specific data stored in a UDR in a structured format and session or state data stored in a UDSF in an unstructured format.
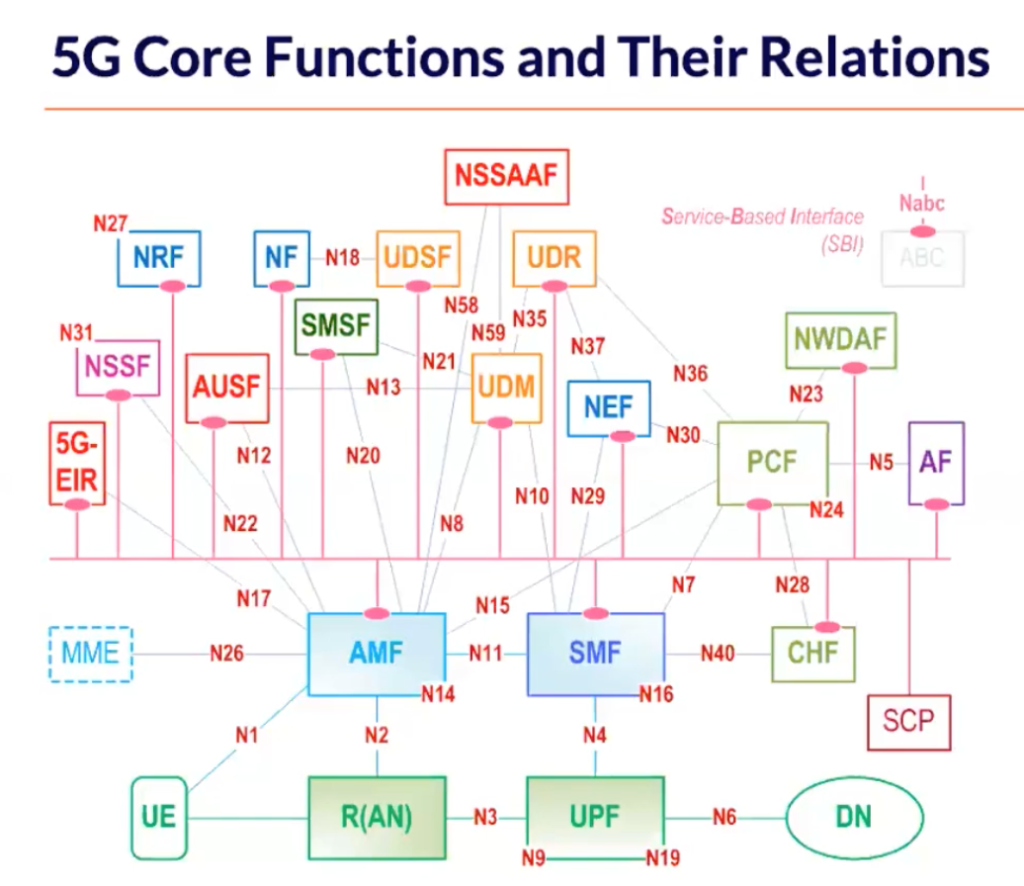
In the talk, Hale goes into detail about all the core network functions and their relationships. And then addresses the tough requirements specifically on UDSF.
Hale noted, “UDSF is near [the] 5G database and it must meet tough requirements such as: carrier grade five nines availability; data access latency of less than one millisecond; ability to scale for very high throughput and massive workloads; ability to handle massive continuous updates; processing power for massive create and delete operations on user context information.”
5G Data Challenges & Solutions
In her talk, Hale detailed several different 5G data challenges:
- Response time: Different response times are required based on the operation being conducted at the network level, service level, or human and internet level
- Transaction Volume: Different network functions have different Transactions Per Hour (TPH) or Transactions Per Second (TPS) requirements
- Throughput falls: Storing large objects reduces throughput in and out of databases, so database operators need to avoid huge databases that would be bottlenecks for service delivery
- Flexibility in stateless approach is stateful: Too much flexibility around the stateless approach leads to many different ways to implement the standards which leads to interoperability issues with data being consumed by the network functions. (Stateless + stateful = Stateful)
She then goes on to describe solutions to these data challenges:
- Protect from the repeating patterns of partitioning
- Keep balance in CAP theorem
- Define standards when things are contradicting
On this last point specifically, Hale describes what has already been done in terms of standards developed by standards developing organizations (SDOs) and implementations by commercial products. But there are still things missing to be addressed.
Introducing the 5G Database Common Interface (5G-DBCI)
At the end of the presentation, Hale describes the collaboration between Rakuten Mobile and Yugabyte, on the 5G Database Common Interface (5G-DBCI). This new standard aims to define database specifications for 5G’s ultra reliability requirement, and for YugabyteDB to be a component of the overall solution to these challenges.
In a nutshell, here are the proposed 5G-DBCI features:
- Data interoperability for 5G core functions
- Service logic for 5G core functions
- Distributed SQL approach for 5G core functions
Want to See More?
Check out all the talks from this year’s Distributed SQL Summit including Pinterest, Mastercard, Comcast, Kroger, and more on our Vimeo channel.